The industrial world is undergoing a massive transformation, and at the heart of this evolution lies Industry 4.0. This revolution, also referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is integrating cutting-edge technologies with traditional manufacturing processes to create smarter, more efficient factories. But how exactly is Industry 4.0 transforming factory floors across the globe? In this blog post, we’ll explore the key elements of Industry 4.0 and examine how it’s reshaping modern manufacturing.
What is Industry 4.0 ?
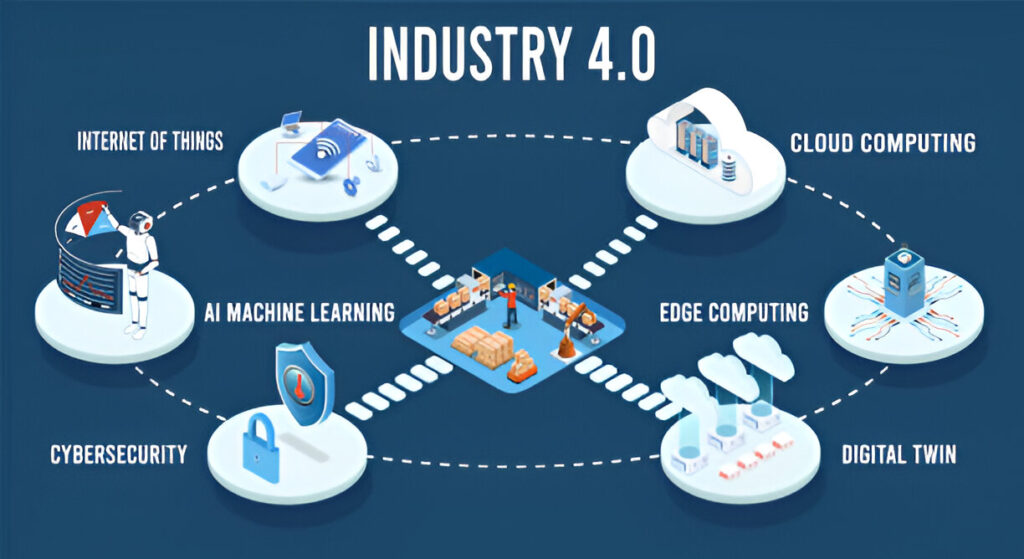
Before diving into its impact, it’s important to understand what Industry 4.0 actually entails. At its core, Industry 4.0 is the blending of the physical and digital worlds, facilitated by advanced technologies such as:
- The Internet of Things (IoT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Big Data Analytics
- Cloud Computing
- Cyber-Physical Systems
- Automation and Robotics
Together, these technologies create interconnected systems that can analyze, communicate, and make decisions autonomously. The result? Smarter factory floors that can adapt to changing conditions, optimize workflows, and reduce downtime.
The Four Stages of the Industrial Revolution
To truly appreciate the significance of Industry 4.0, it helps to briefly review the history of industrial revolutions:
- Industry 1.0 (Mechanization): Beginning in the late 18th century, the first industrial revolution was defined by the introduction of steam power and mechanized production.
- Industry 2.0 (Mass Production): The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the advent of electricity, which led to the rise of mass production through assembly lines.
- Industry 3.0 (Automation): From the 1960s onward, the third industrial revolution brought about the use of computers, automation, and electronics to further enhance manufacturing.
- Industry 4.0 (Smart Manufacturing): The current era is focused on the integration of digital technologies into physical systems, leading to the creation of intelligent factories.
Key Technologies Driving Industry 4.0
1. The Internet of Things (IoT)
One of the most impactful technologies of Industry 4.0 is the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT refers to the network of connected devices that collect and exchange data. In a factory setting, IoT devices can include sensors, machines, and other equipment that communicate with each other in real-time.
For example, IoT sensors on factory floors can monitor machine performance, detect anomalies, and predict potential failures before they occur. This predictive maintenance approach can drastically reduce downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring that machines operate at peak efficiency.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are critical components of Industry 4.0. These technologies enable machines to not only follow predefined instructions but also to learn from data and adapt over time. AI can optimize production schedules, streamline supply chains, and even improve product quality by analyzing data collected from various sources.
For instance, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns in production data that humans might miss, allowing manufacturers to enhance production efficiency and reduce waste.
3. Automation and Robotics
Automation has been part of factory floors for decades, but with Industry 4.0, automation is reaching new heights. Robots are becoming more advanced, capable of performing complex tasks that once required human intervention. Collaborative robots (cobots) are designed to work alongside human workers, increasing productivity without compromising safety.
Automation also extends beyond physical tasks. In an Industry 4.0-enabled factory, entire processes can be automated, from order processing to inventory management.
4. Big Data and Analytics
Data is at the heart of Industry 4.0. The massive amounts of data generated by connected devices, machines, and systems are analyzed using advanced analytics tools. Big Data analytics helps manufacturers make informed decisions, identify inefficiencies, and optimize processes in real time.
For example, by analyzing data from IoT sensors, manufacturers can adjust production parameters to reduce energy consumption, increase throughput, and improve product quality.
5. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure necessary to store, process, and analyze the vast amounts of data generated in Industry 4.0 environments. Cloud-based platforms enable manufacturers to access real-time data from any location, allowing for better decision-making and collaboration across different sites.
Cloud computing also supports the scalability of Industry 4.0 technologies, enabling factories to easily integrate new devices and systems as their operations grow.
6. Cyber-Physical Systems
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) refer to the integration of physical processes with digital control systems. These systems use feedback loops to monitor and control physical processes in real-time. On the factory floor, CPS allows for greater flexibility and adaptability, as machines can be adjusted on the fly based on real-time data.
For example, if a machine detects a defect in a product, it can automatically halt production and notify the operator, ensuring that issues are addressed immediately.
How Industry 4.0 is Transforming Factory Floors
The implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies is having a profound impact on factory floors, resulting in:
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity due to Industry 4.0
One of the most significant benefits of Industry 4.0 is the dramatic increase in efficiency and productivity. Automation, AI, and IoT technologies allow manufacturers to optimize their production processes and reduce downtime. Predictive maintenance, in particular, ensures that machines are repaired before they break down, preventing costly disruptions.
2. Enhanced Product Quality
By leveraging AI and Big Data analytics, manufacturers can improve product quality through real-time monitoring and adjustments. For example, machine learning algorithms can identify defects early in the production process, allowing for quick corrections and minimizing waste. This level of quality control is particularly valuable in industries where precision is critical, such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
3. Reduced Operational Costs
While the initial investment in Industry 4.0 technologies may be significant, the long-term cost savings are substantial. Predictive maintenance reduces repair costs, automation decreases labor expenses, and energy-efficient processes lower utility bills. Additionally, by optimizing supply chains, manufacturers can reduce excess inventory and minimize waste.
4. Better Decision-Making
With access to real-time data from every corner of the factory, managers can make informed decisions faster. For instance, if a bottleneck occurs in the production line, the system can automatically suggest adjustments to optimize the workflow. This level of transparency ensures that operations run smoothly, even in the face of unexpected challenges.
5. Flexibility and Customization
Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to shift from mass production to mass customization. With technologies like 3D printing and AI-driven design, factories can quickly adapt to changing customer demands and produce highly customized products without sacrificing efficiency.
6. Safer Work Environments
Automation and robotics not only increase productivity but also improve safety on factory floors. By taking over dangerous or repetitive tasks, machines reduce the risk of workplace accidents. In addition, IoT sensors can monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature and air quality, ensuring that the work environment remains safe for employees.
Challenges of Implementing Industry 4.0
Despite the numerous benefits, adopting Industry 4.0 comes with its own set of challenges. These include:
- High initial costs: The implementation of advanced technologies requires significant investment in infrastructure, training, and integration.
- Data security concerns: With increased connectivity comes a higher risk of cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive data is crucial for ensuring the integrity of operations.
- Skill gaps: As factories become more technologically advanced, there is a growing need for workers with specialized skills in areas like AI, data analytics, and cybersecurity.
However, these challenges can be overcome through strategic planning, investment in employee training, and collaboration with technology partners.
Conclusion on Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is undoubtedly revolutionizing factory floors, bringing about unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. By embracing advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation, manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market. While challenges remain, the long-term benefits of Industry 4.0 make it a transformative force that is here to stay.
References of Industry 4.0
For more insights into how emerging technologies are impacting various sectors, check out our Top 5 Emerging Trends in the Manufacturing Sector for 2024 (inbound link).
For further reading on the global impact of Industry 4.0, explore this article on Forbes.